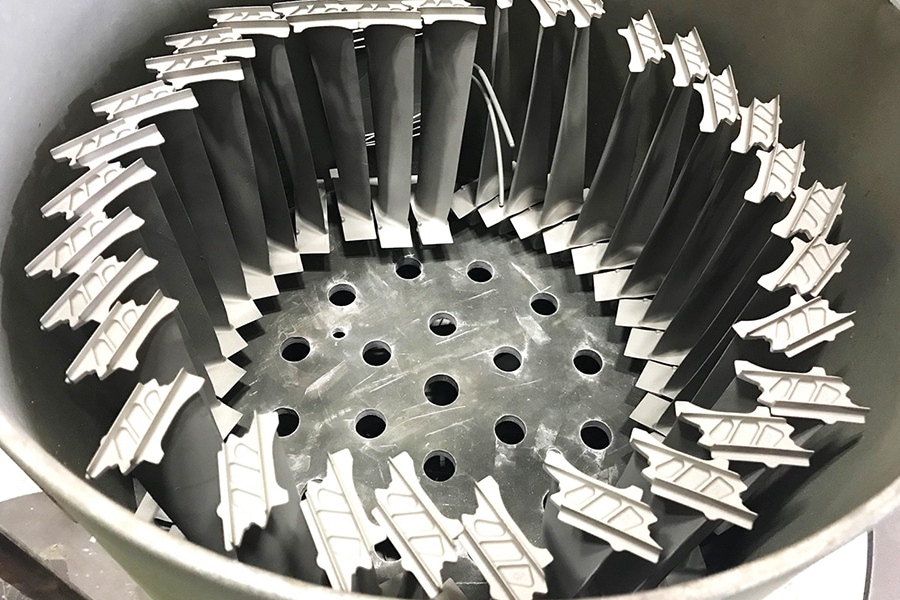
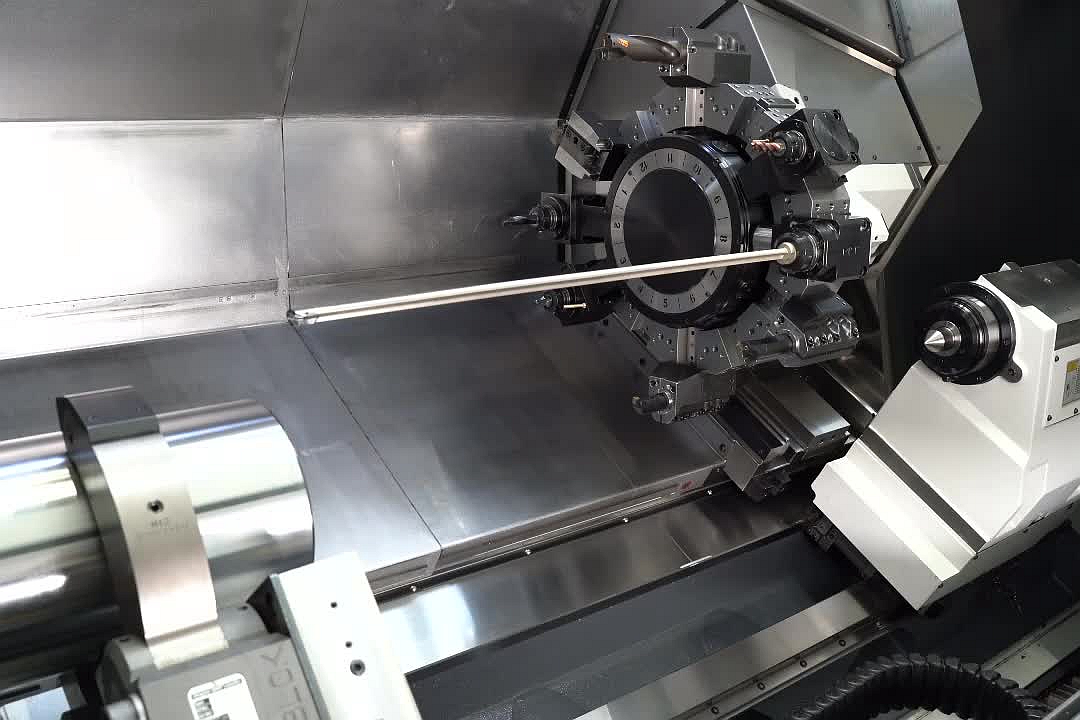
Custom Marine Superalloy Parts Factory
Custom High Temperature Alloy Chemical Processing Parts Manufacturing
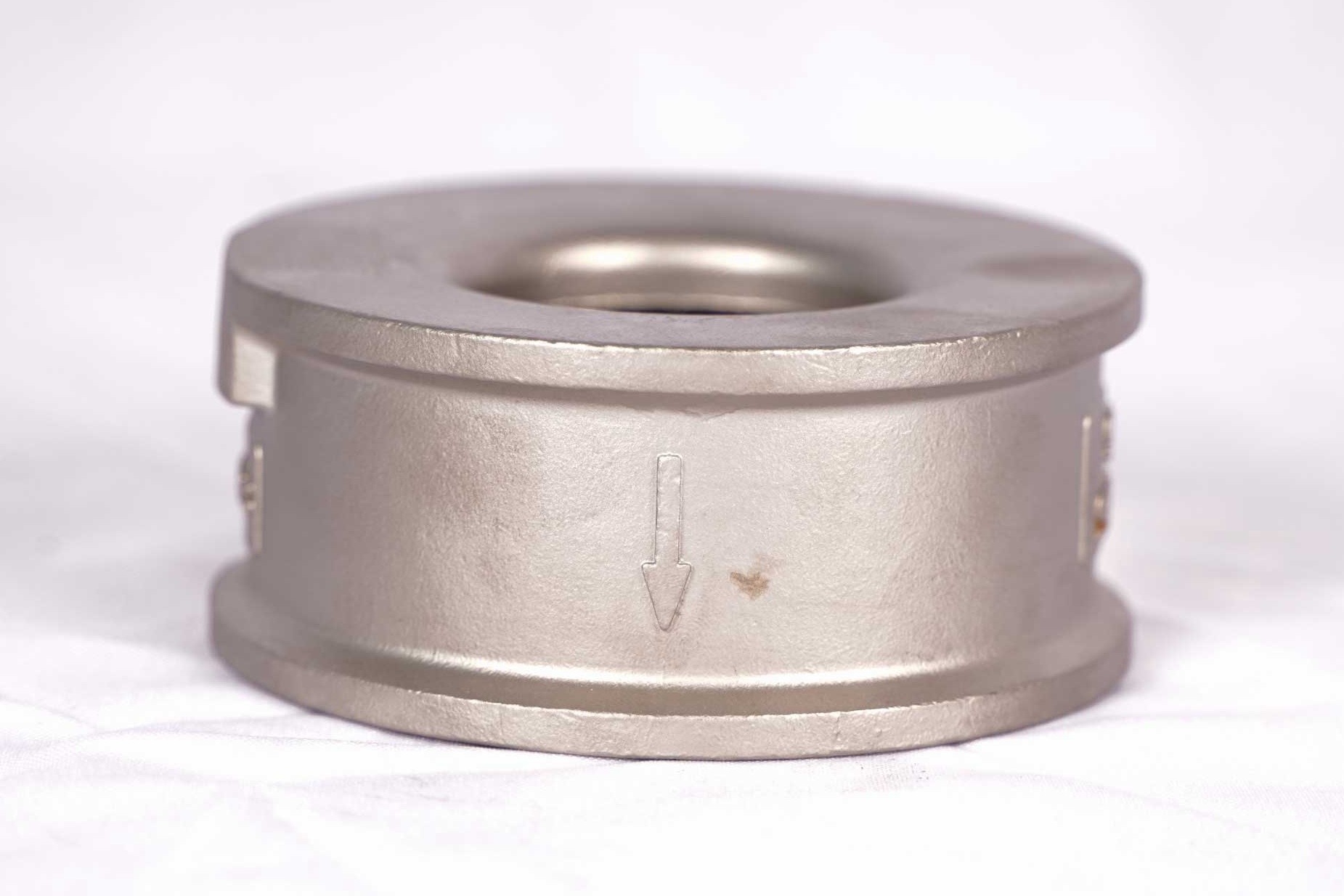
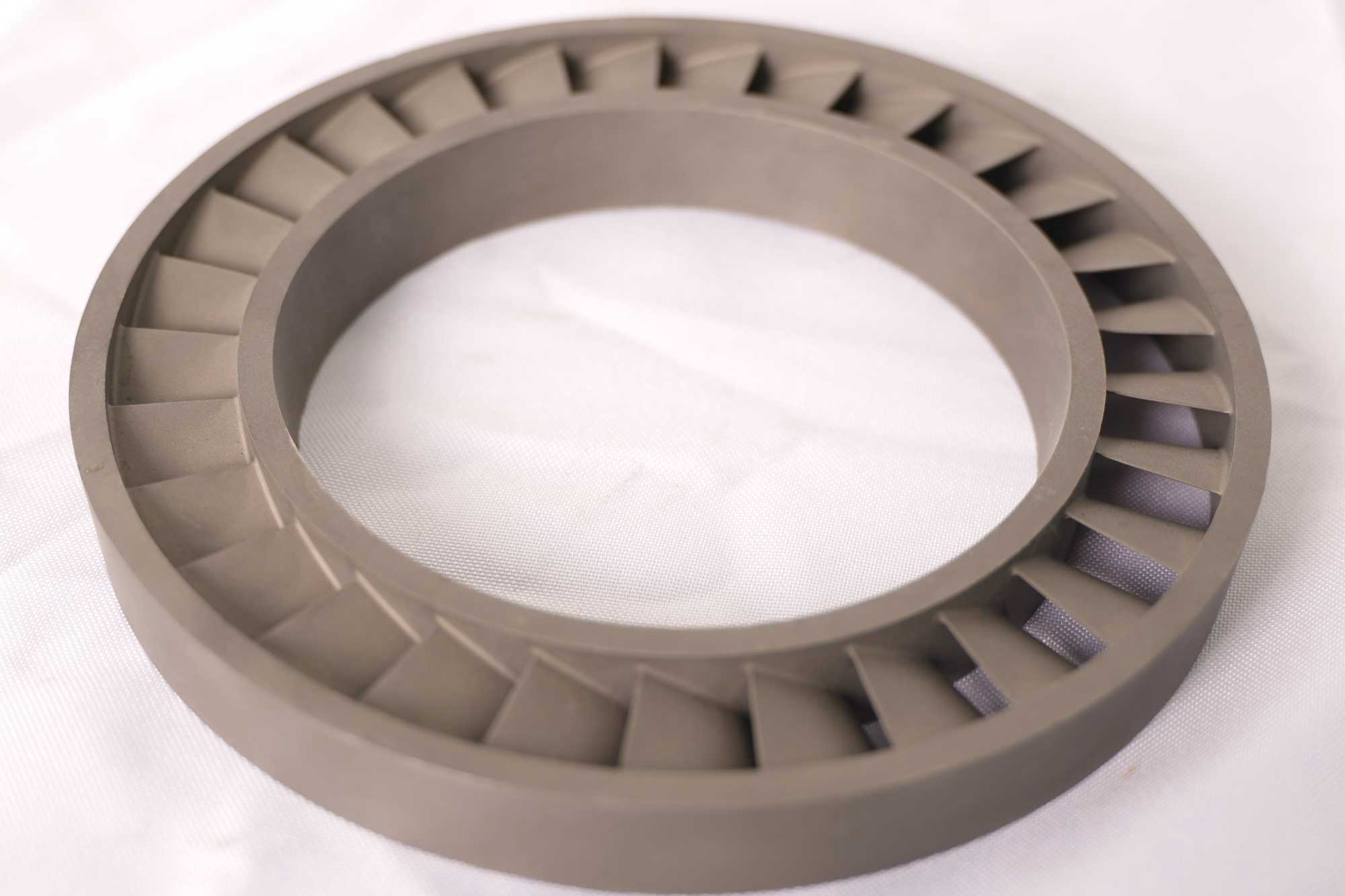
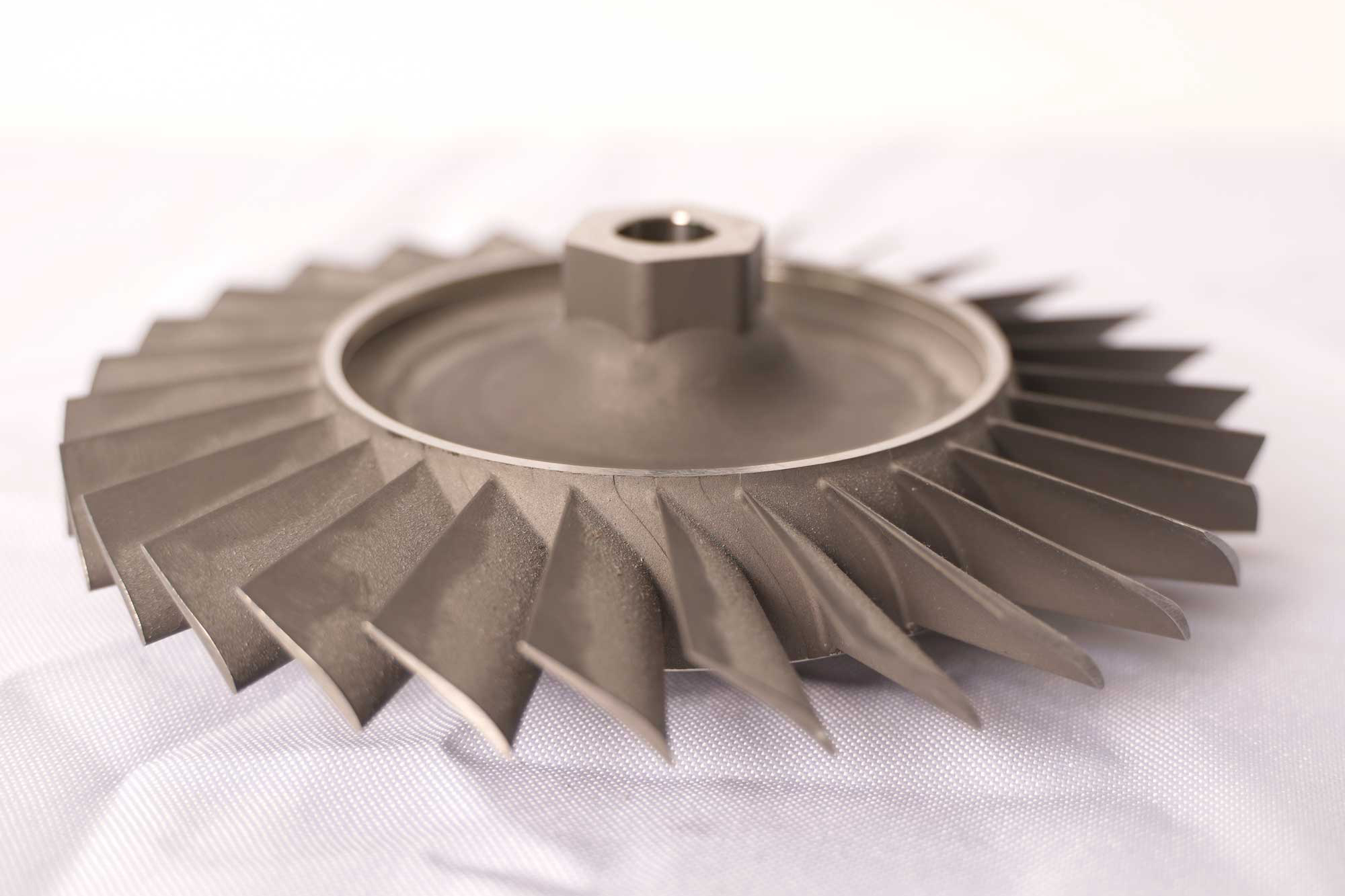
Neway offers manufacturing processes like vacuum investment casting, directional casting, powder metallurgy, precision forging, and superalloy 3D printing. They produce custom chemical processing parts such as corrosion-resistant valves, impellers, nozzles, and pump housings.
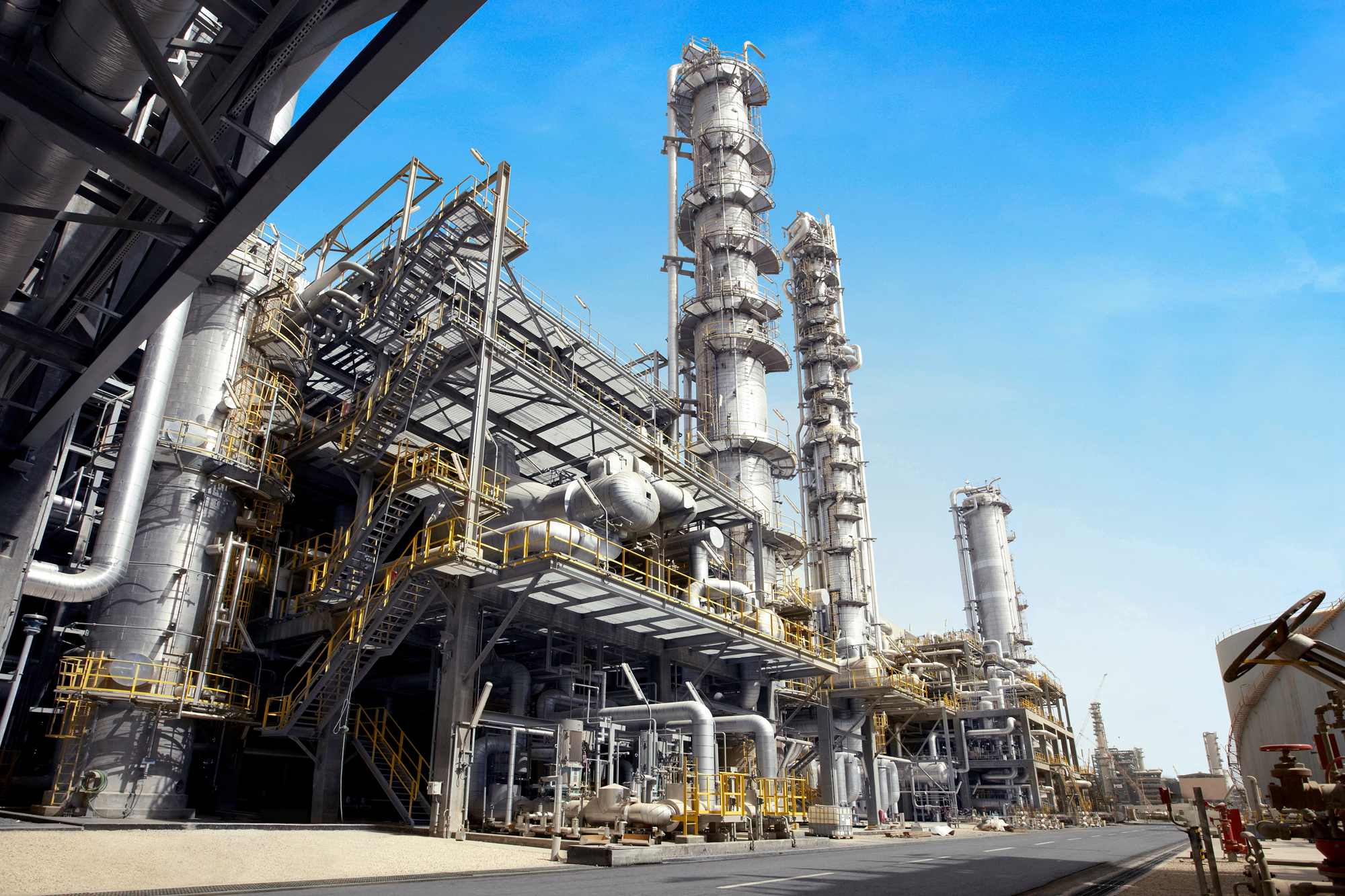

High Temperature Alloy Chemical Processing Parts Manufacturing Solutions
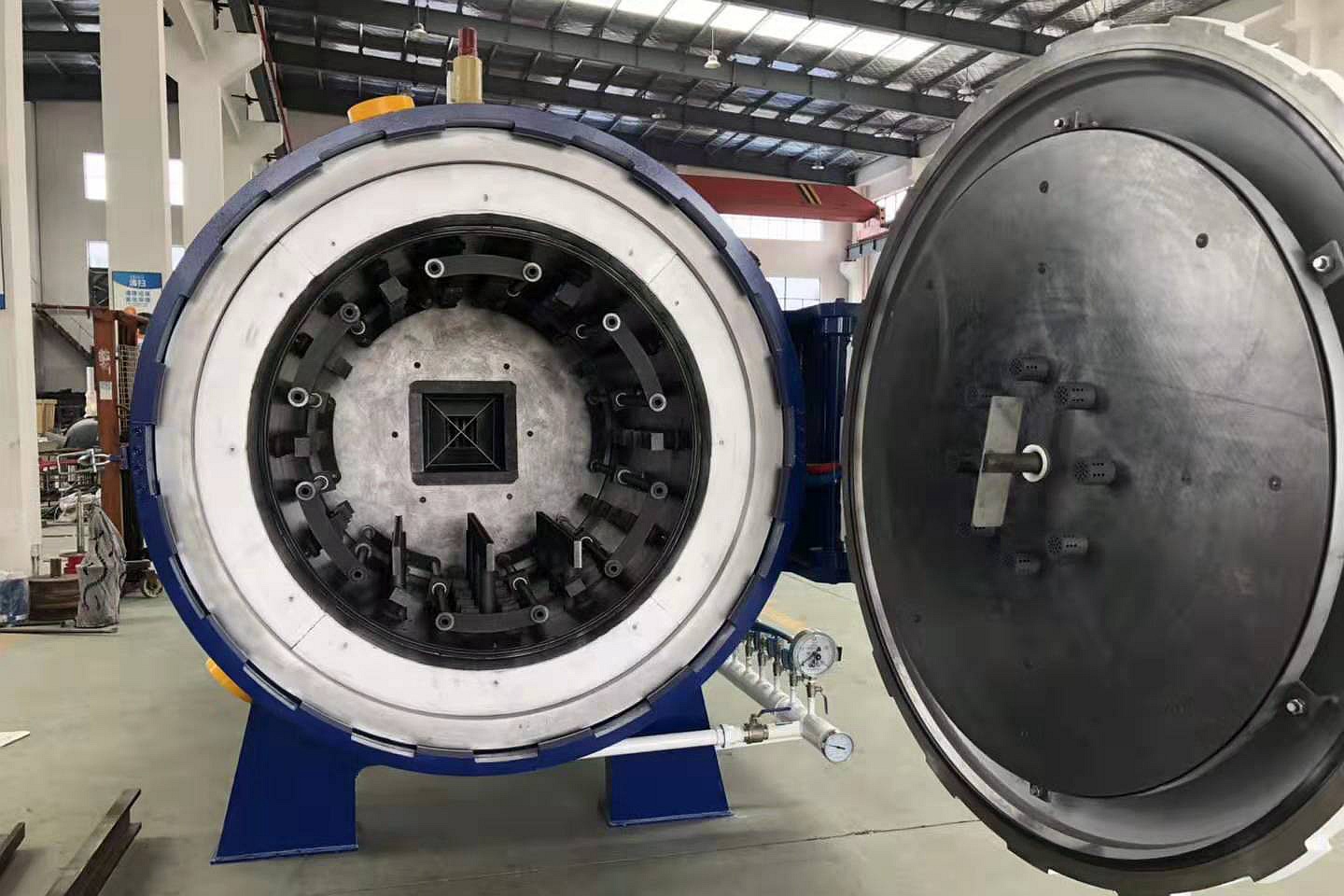
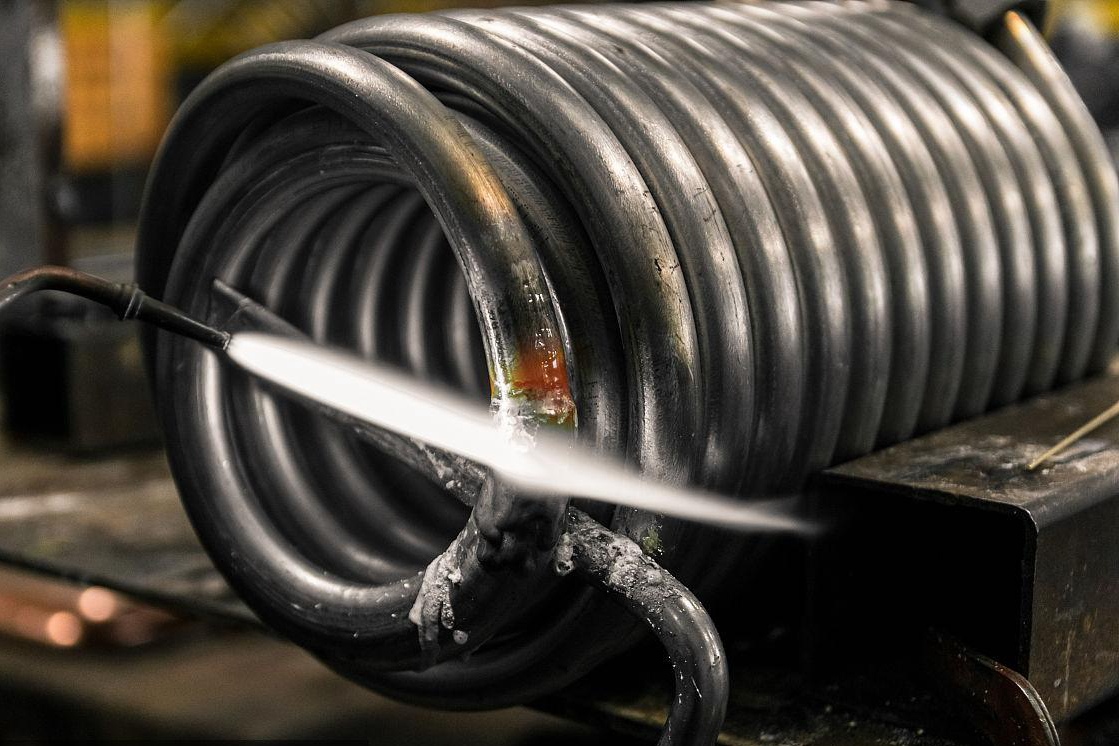
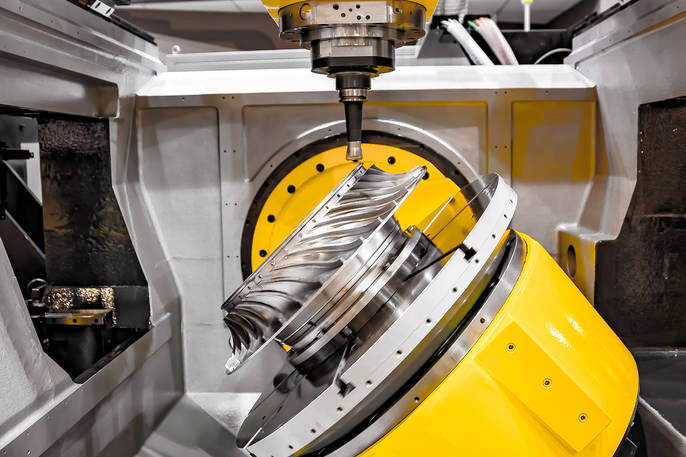
Neway uses several processes for high-temperature alloy chemical processing parts, including vacuum investment casting, directional casting, and equiaxed crystal casting for complex shapes. Powder metallurgy and precision forging ensure strength, while CNC machining and 3D printing enable high-precision components. Post-processes like heat treatment, hot isostatic pressing (HIP), and welding enhance durability and resistance to harsh chemical environments.
Chemical Processing Industry Superalloy Selection
The chemical processing industry uses superalloys like Hastelloy, Inconel, Monel, and Titanium for their superior corrosion resistance, strength, and ability to withstand harsh chemicals and high temperatures. These materials are essential in reactors, heat exchangers, valves, and piping systems, ensuring durability and efficiency in corrosive environments. Their reliability enhances safety and longevity in chemical processing and refining applications.
Chemical Processing Parts Post Process and Surface Treatment Solutions
Neway offers post-processing like hot isostatic pressing (HIP), heat treatment, and welding for high-temperature alloy valves, nozzles, and impellers in the chemical processing industry. Surface treatments such as thermal barrier coatings (TBC) and anti-corrosion coatings enhance durability and resistance to harsh chemical environments, ensuring longer component life under extreme temperatures and corrosive conditions.
High Temperature Alloy Components In Chemical Processing Industry
Neway has manufactured high-temperature alloy components like corrosion-resistant valves, impellers, nozzles, and pump housings for the chemical processing industry. These are produced using vacuum investment casting, directional casting, and precision forging, followed by CNC machining and post-processing like heat treatment, welding, and hot isostatic pressing (HIP) to ensure durability, precision, and resistance to extreme environments.

learn more
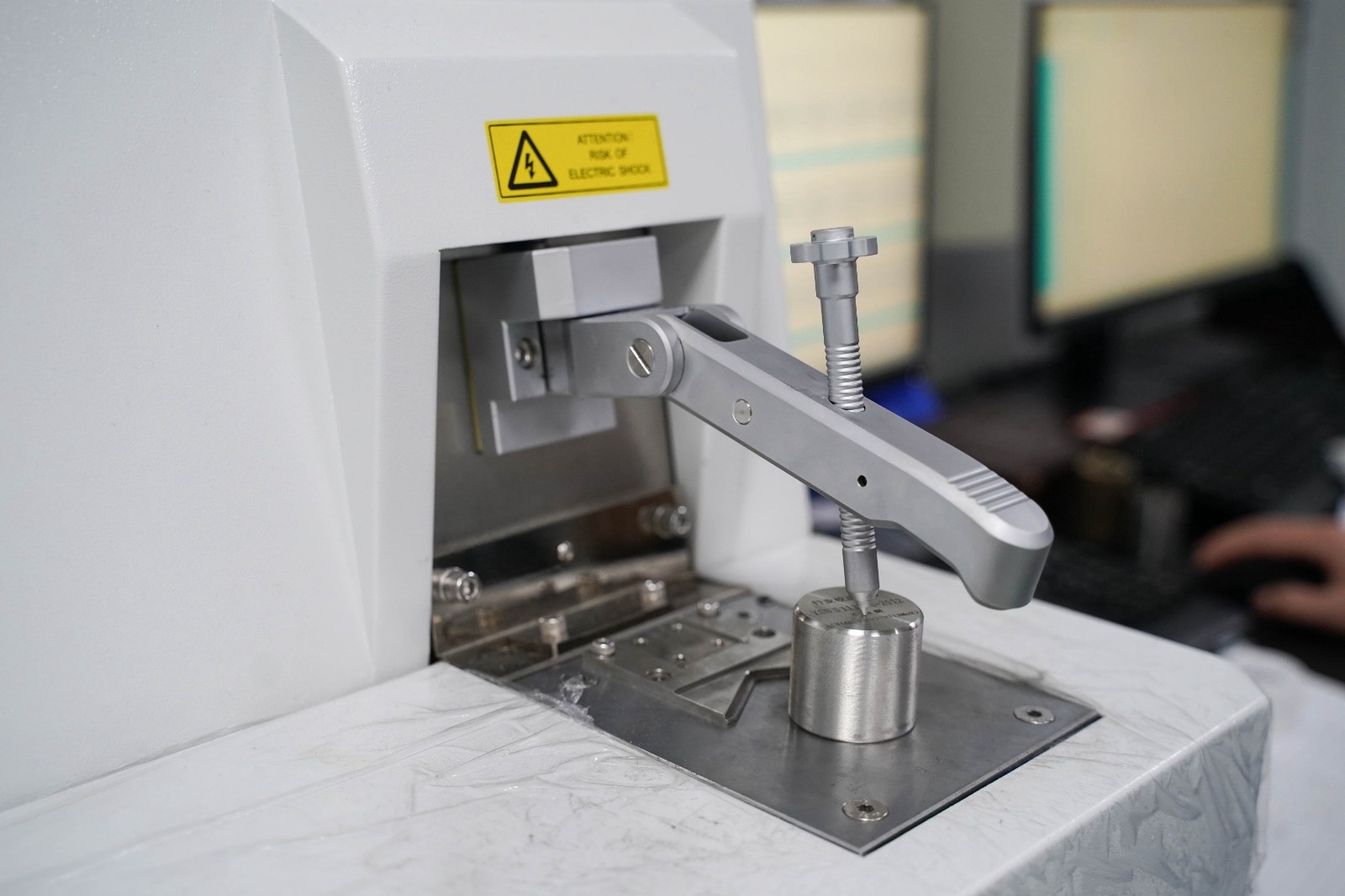
Direct Reading Spectrometer

learn more
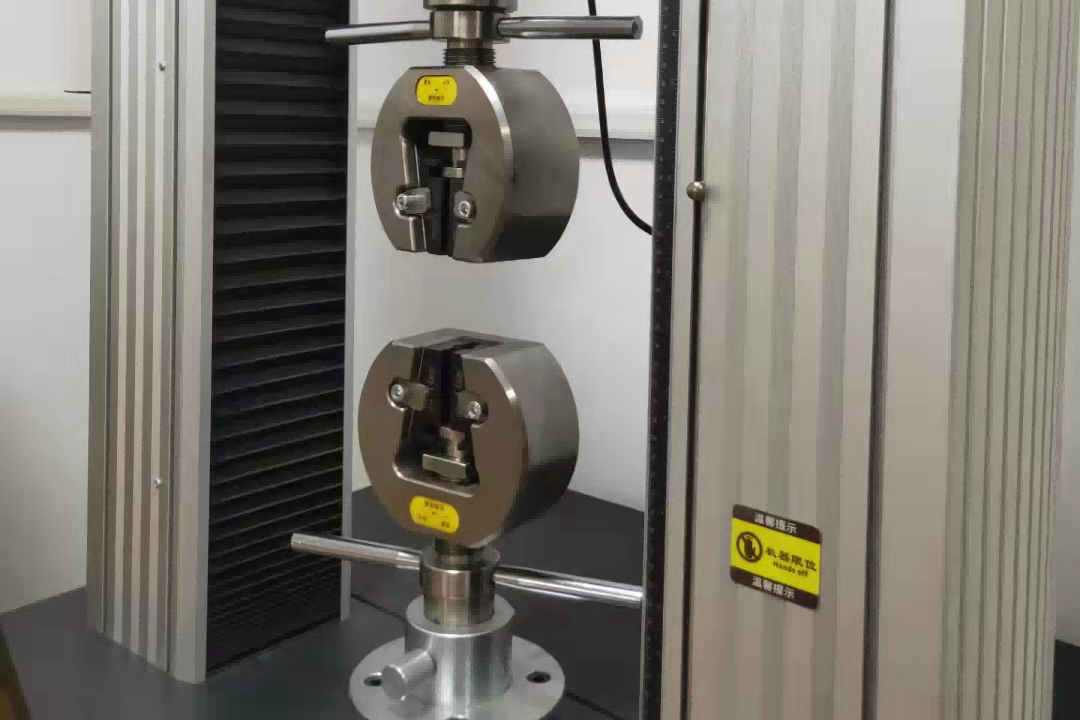
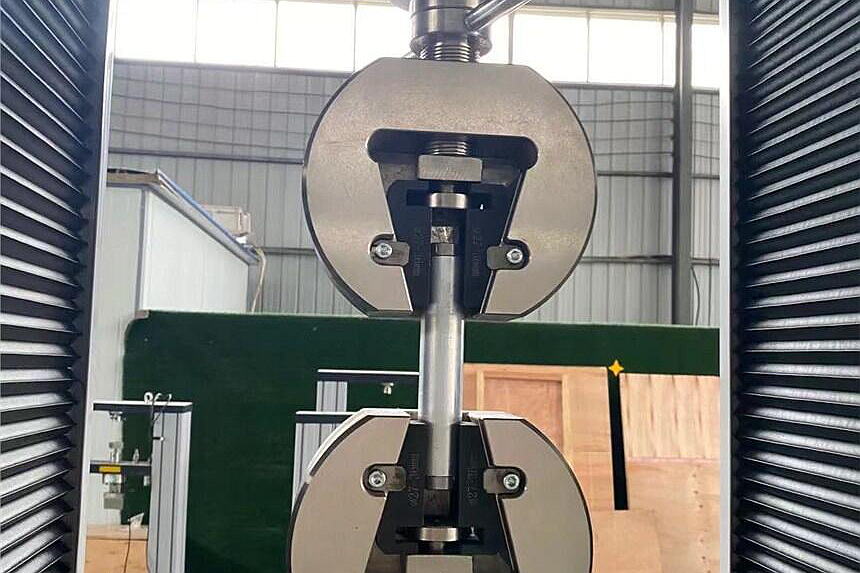
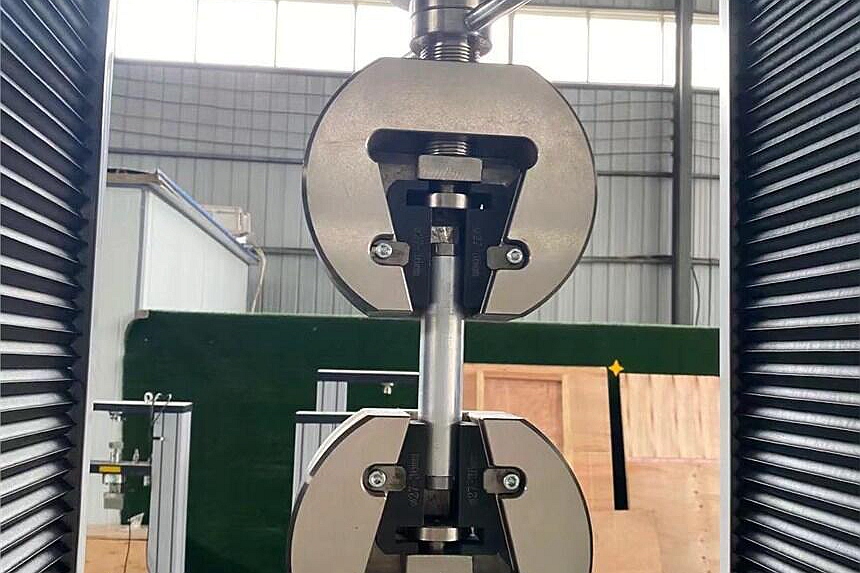
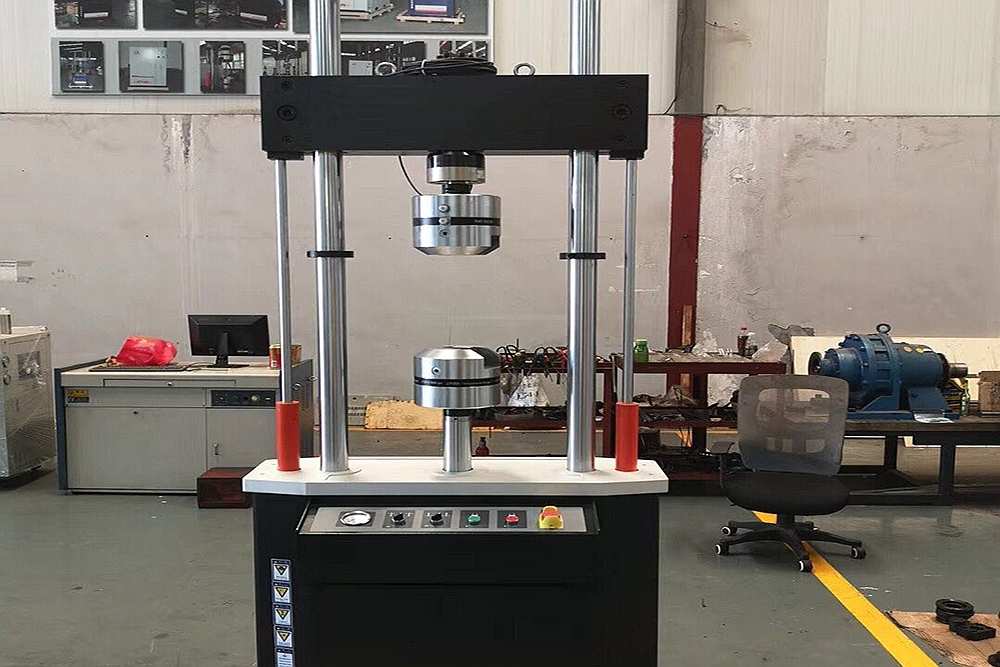
Tensile Testing Machine Checking
learn more
X-ray Checking

learn more
Thermal Physical Properties Test Platform

learn more
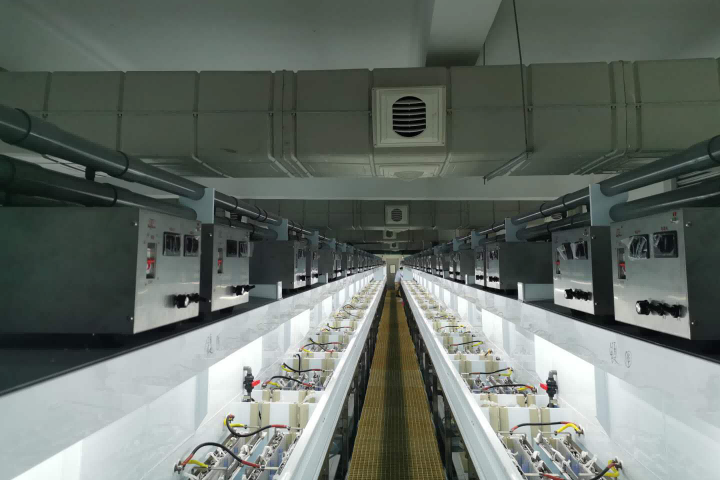
Corrosion Production Line

learn more
Dynamic and Static Fatigue Tester
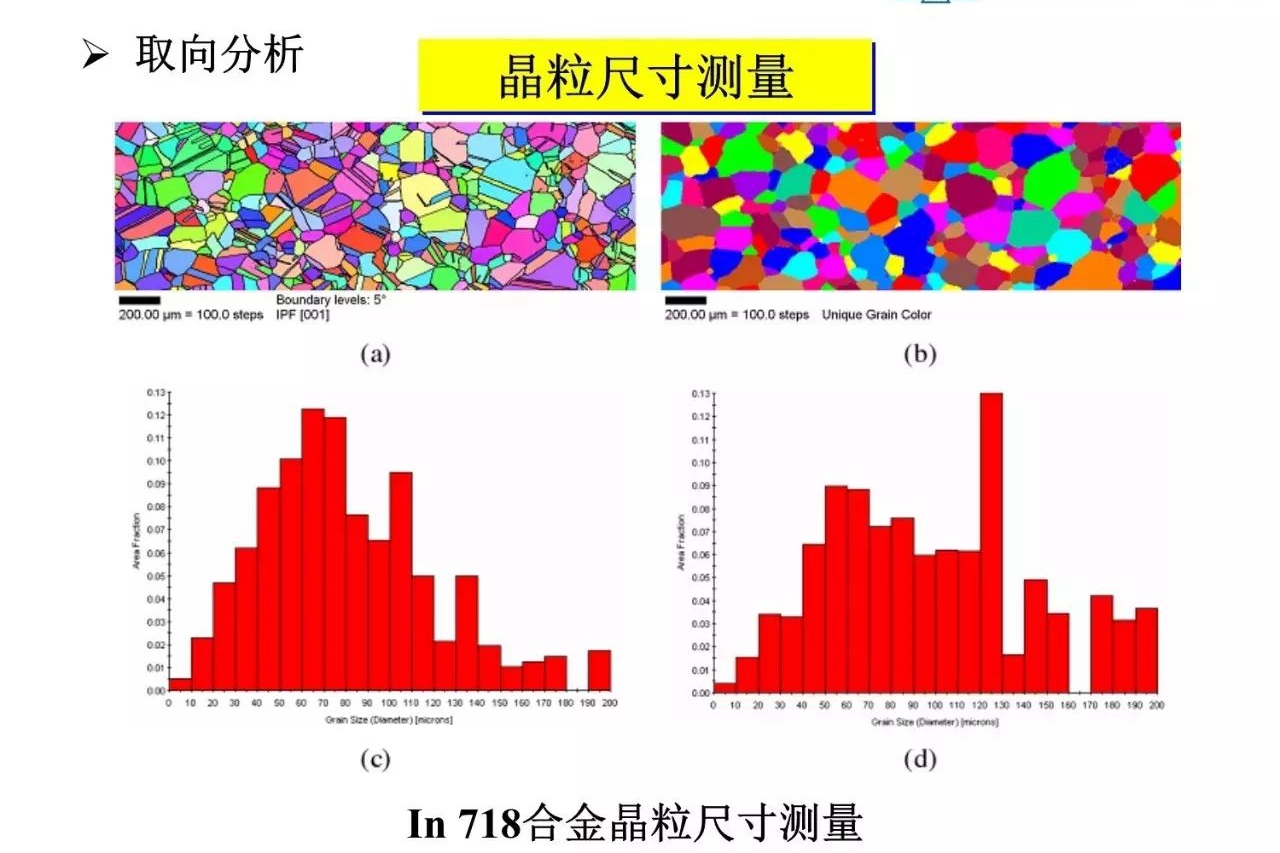
learn more
Electron Backscattering Diffractometer (EBSD)
learn more
Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometer (ICP-OES)
learn more
3D Scanning Measuring Instrument Checking
learn more
Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM)
learn more
Glow Discharge Mass Spectrometer (GDMS)
learn more
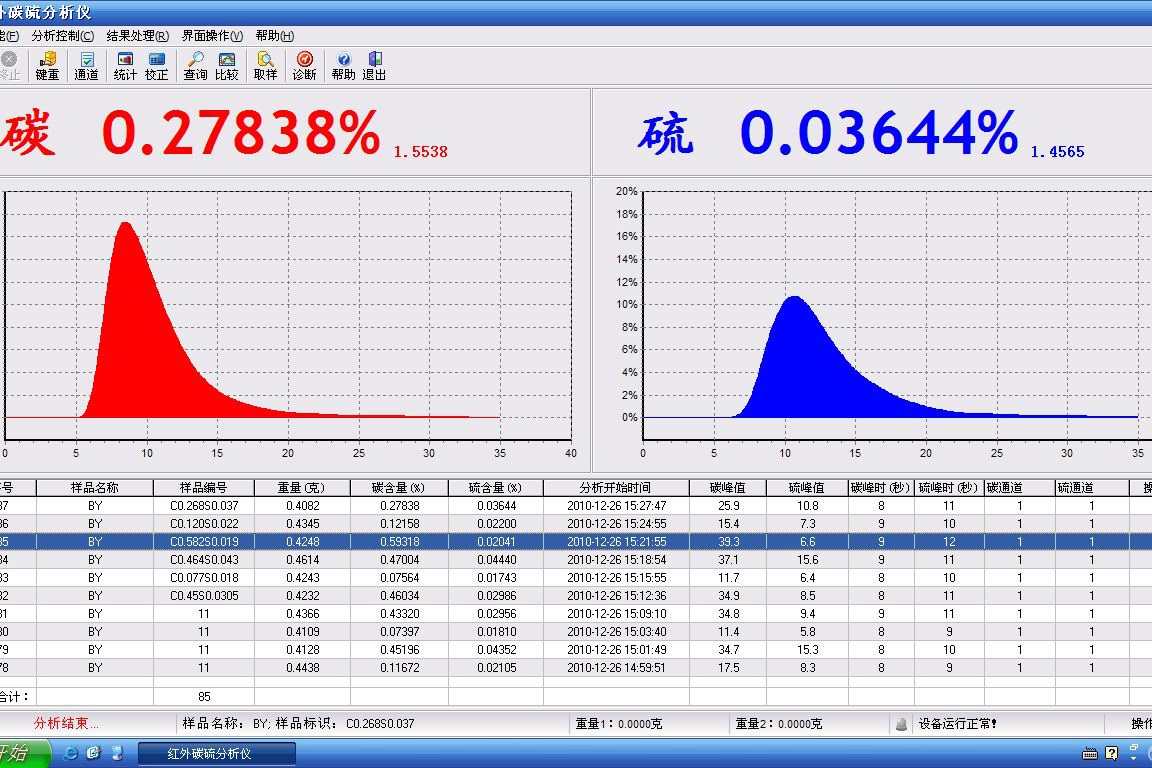
Carbon Sulfur Analyzer Checking
learn more
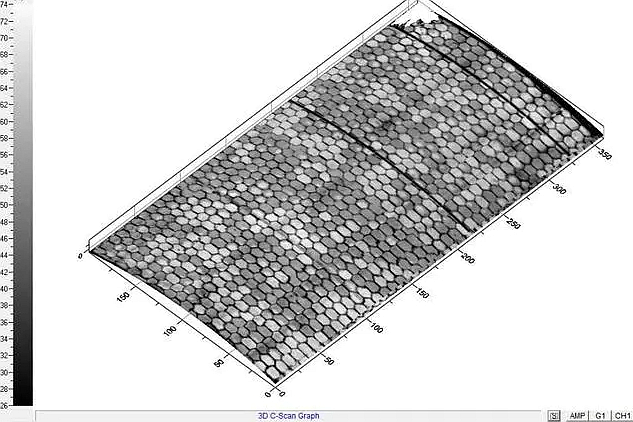
Water Immersion Ultrasonic Inspection

learn more
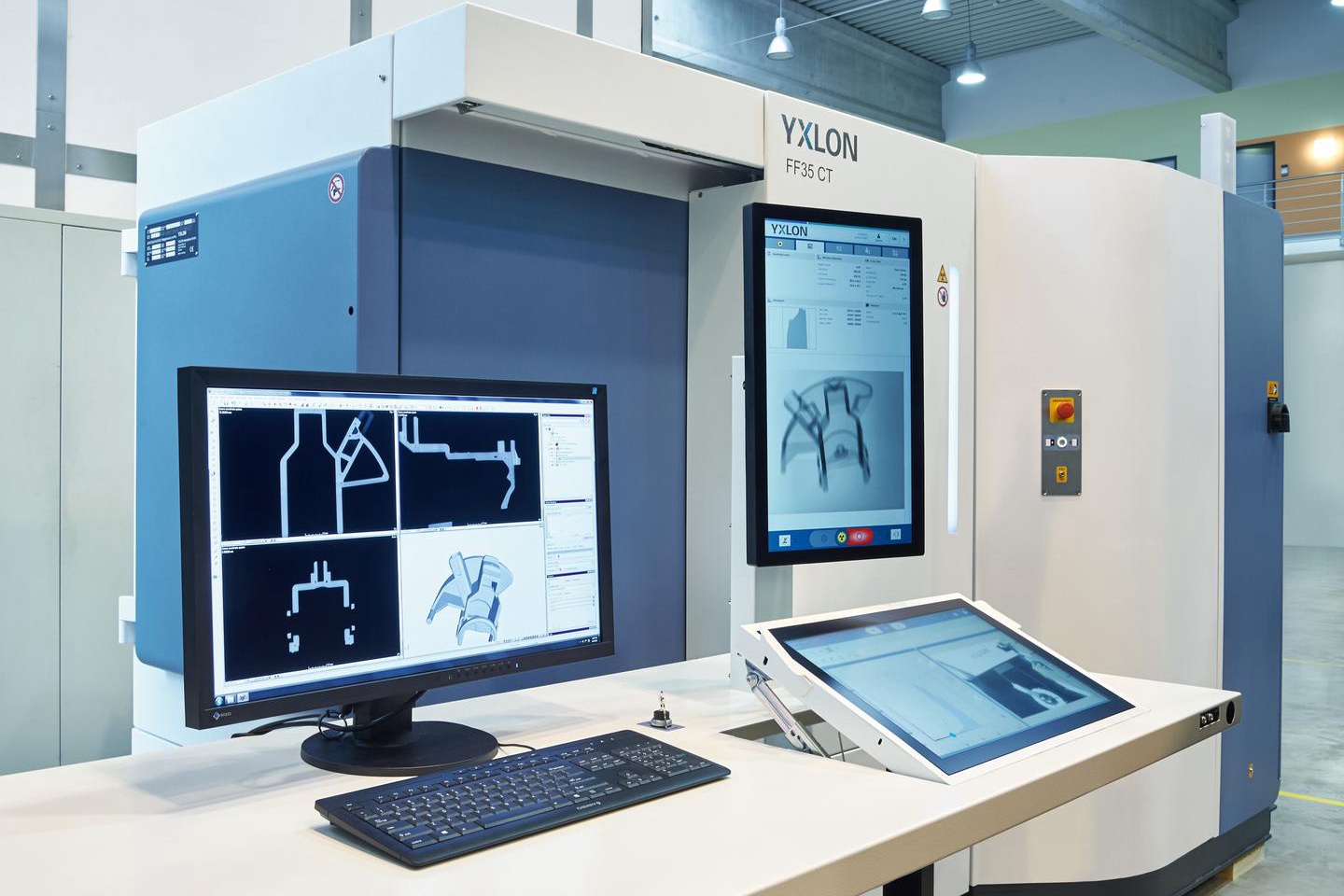
Line Array Industrial CT(GE)

learn more
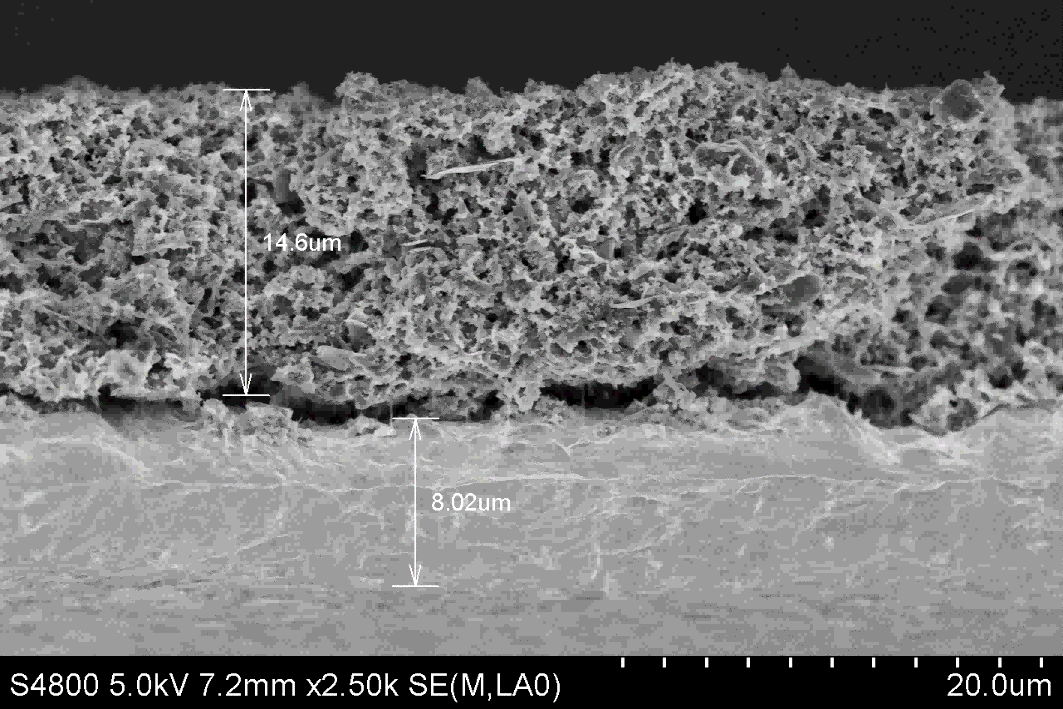
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Checking

learn more
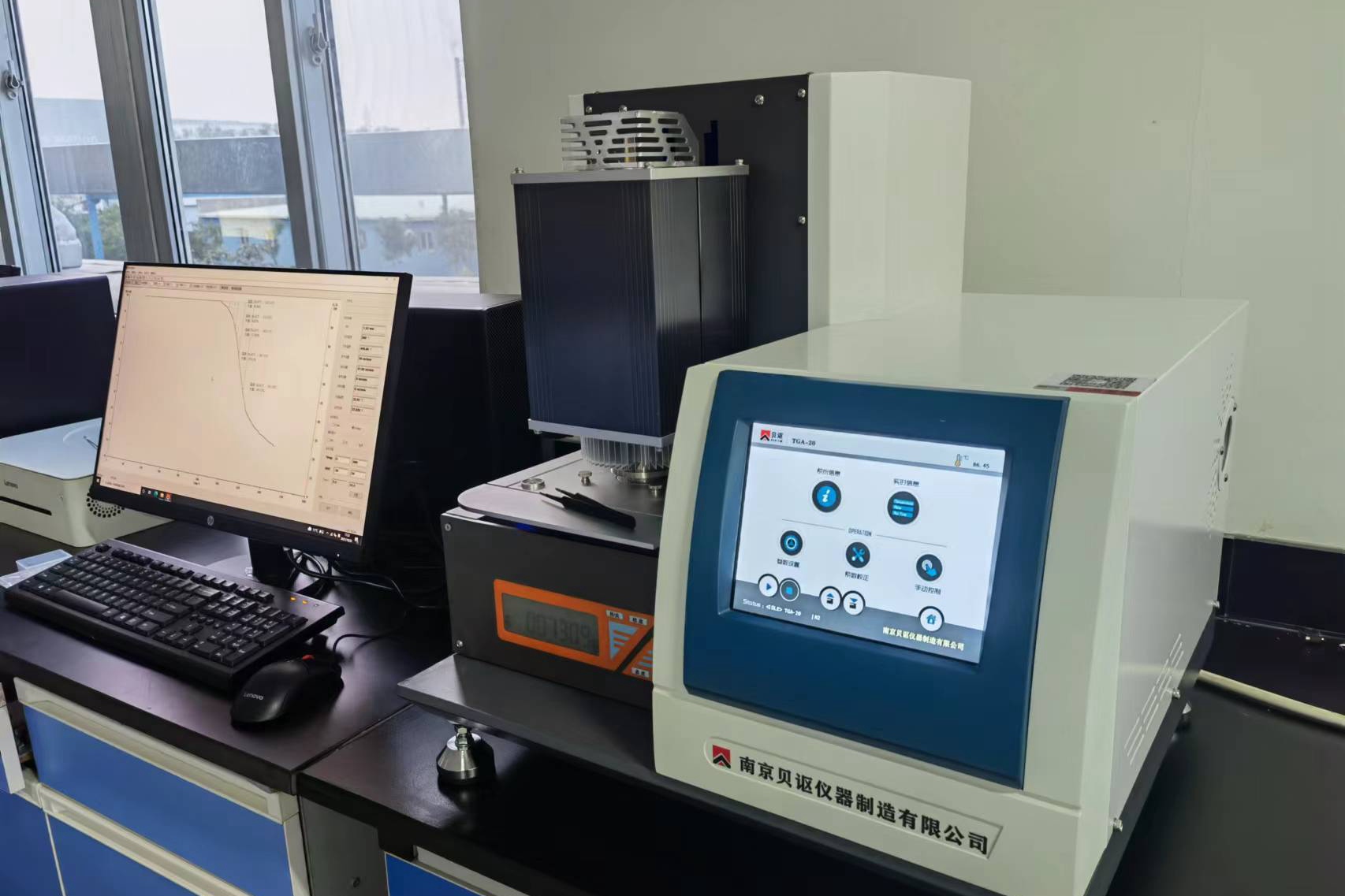
Simultaneous Thermal Analyzer (STA) Checking
learn more
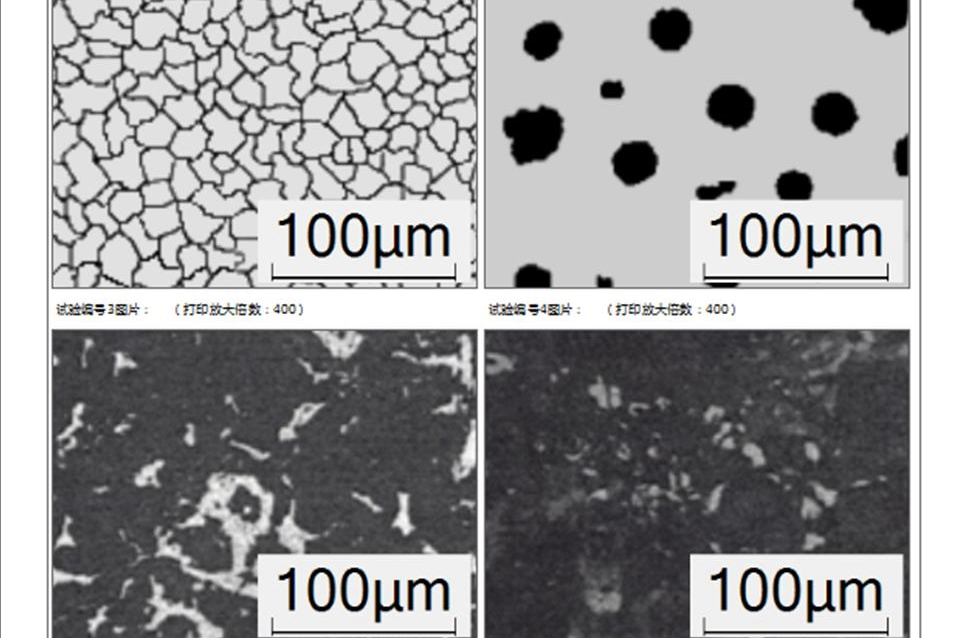
Metallographic Microscopy Checking
learn more
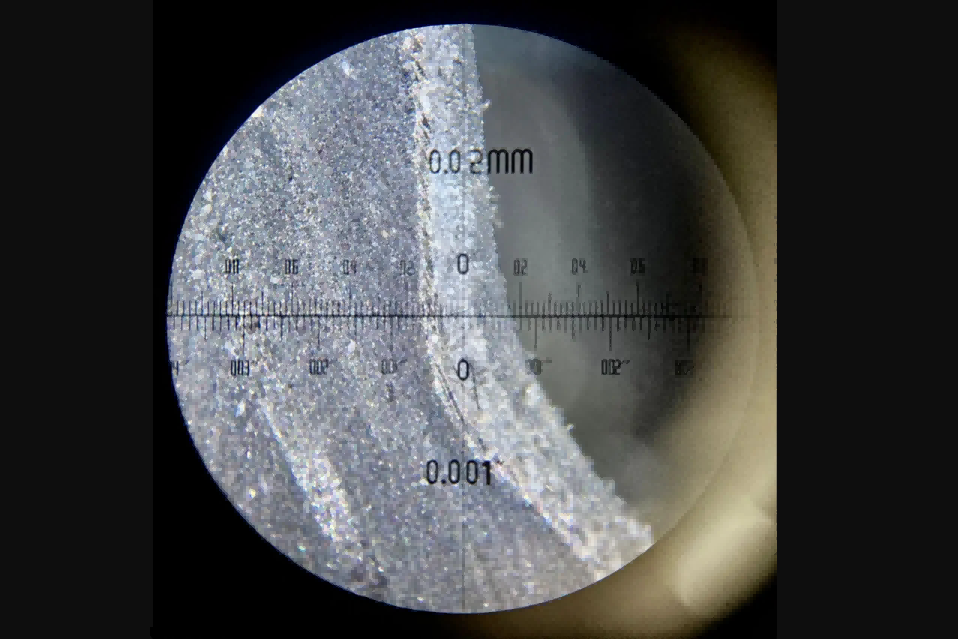
Stereo Microscope Checking
learn more
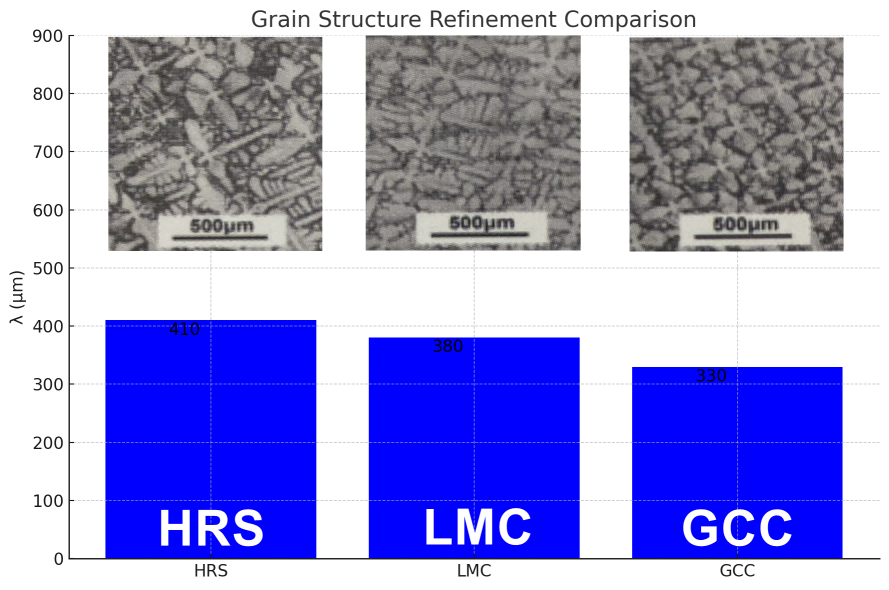
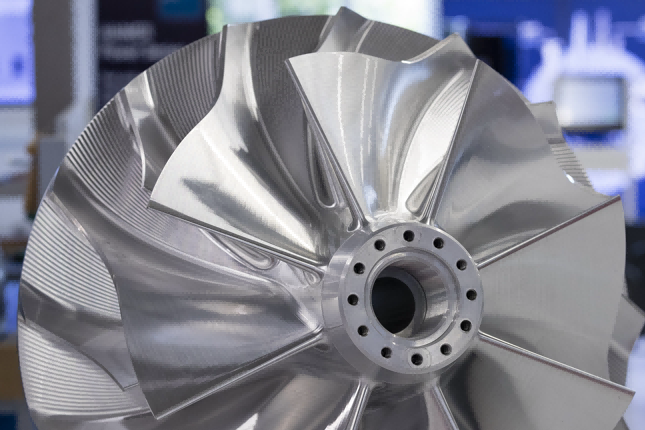
New Technology

learn more
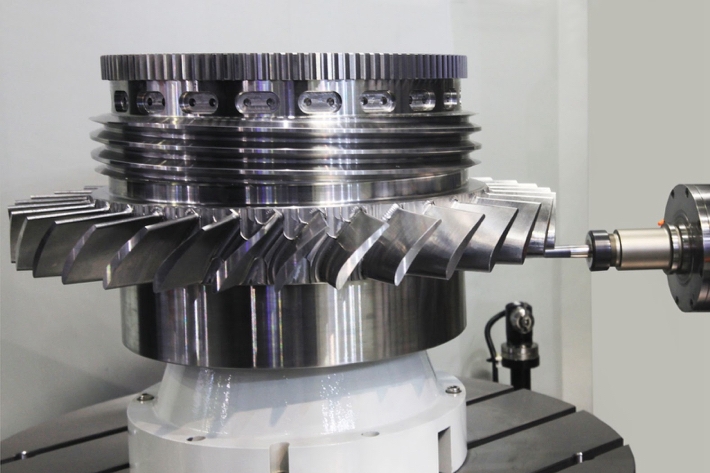
Products Gallery

learn more
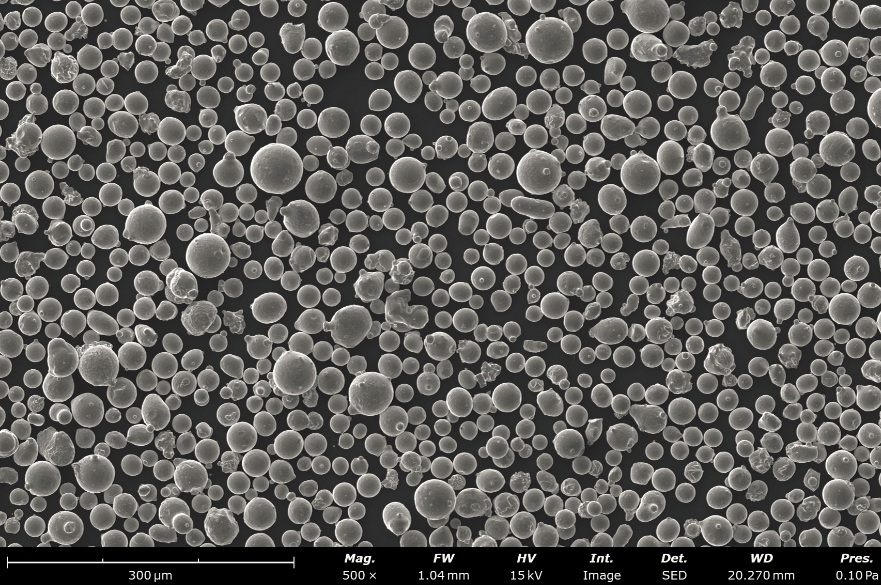
Various Industries
learn more
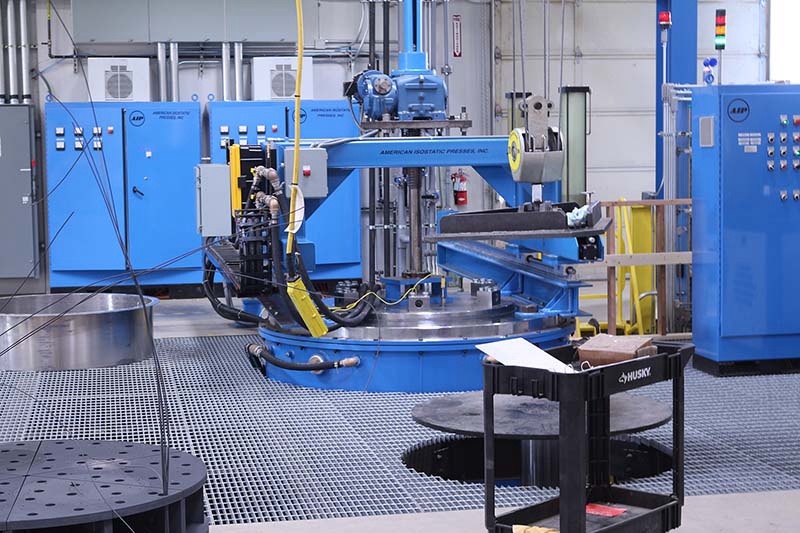
Surface Finishings

learn more
Post-Process
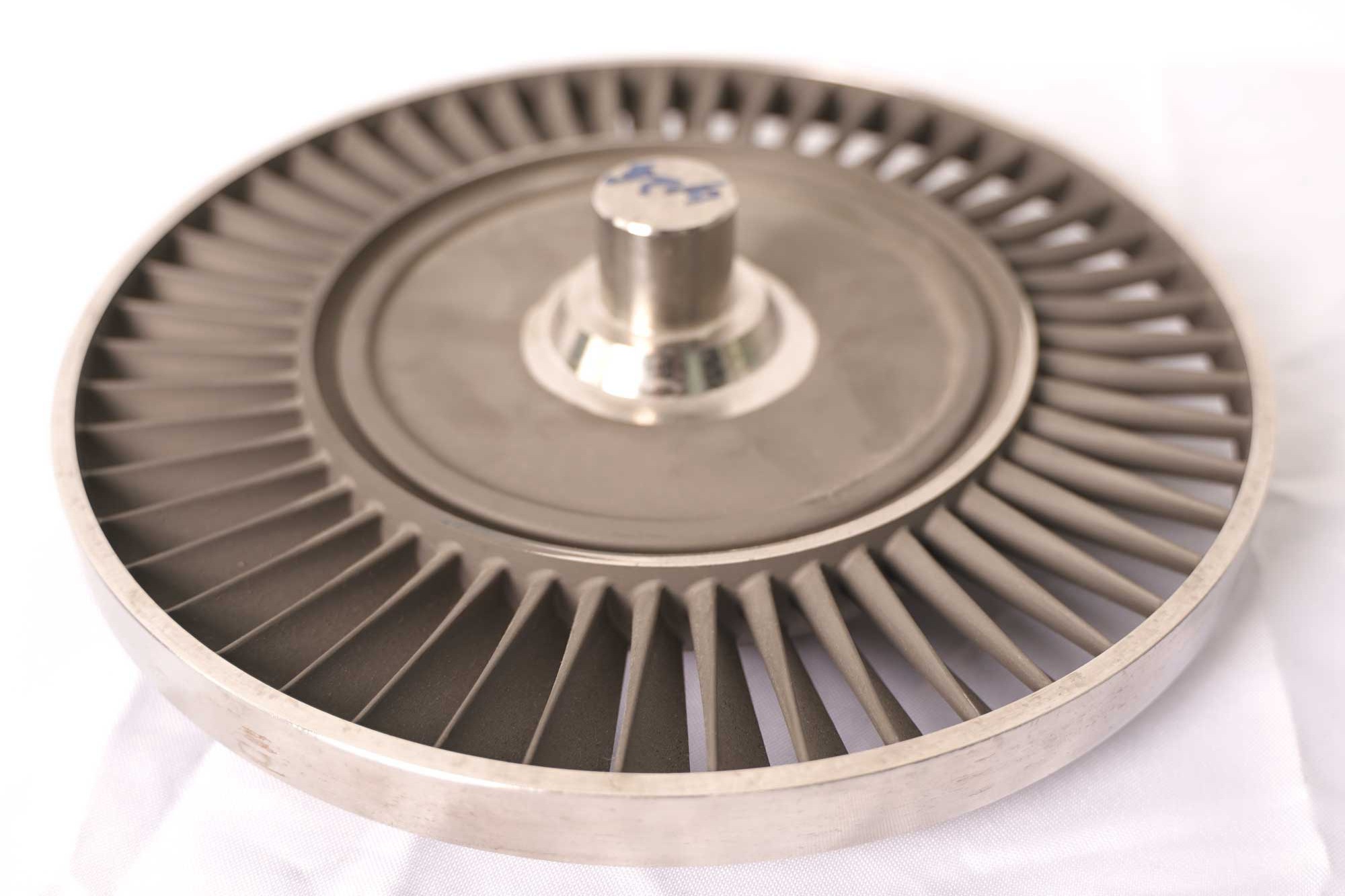

learn more
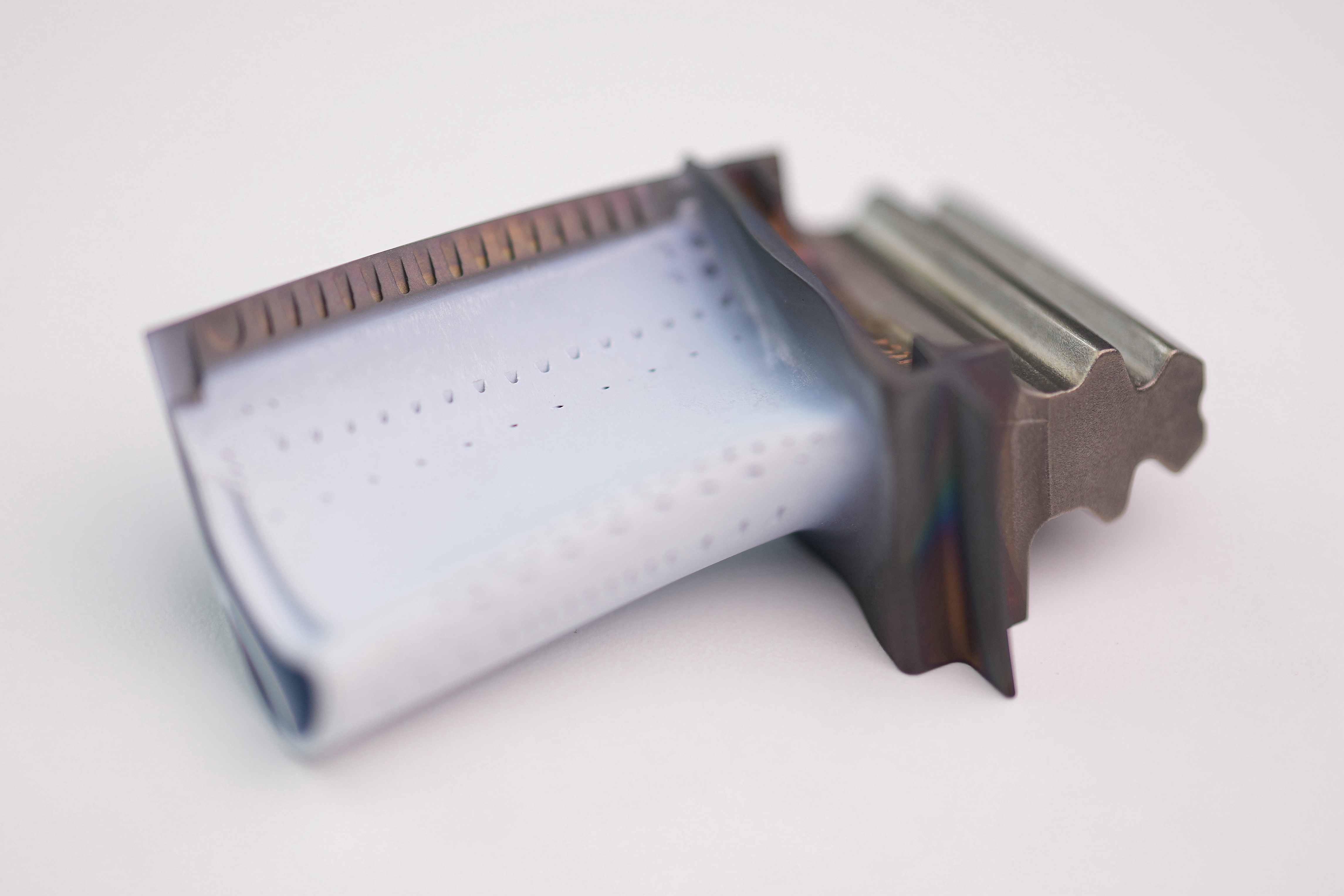
Manufacturing Technology
learn more
R&D and Simulation
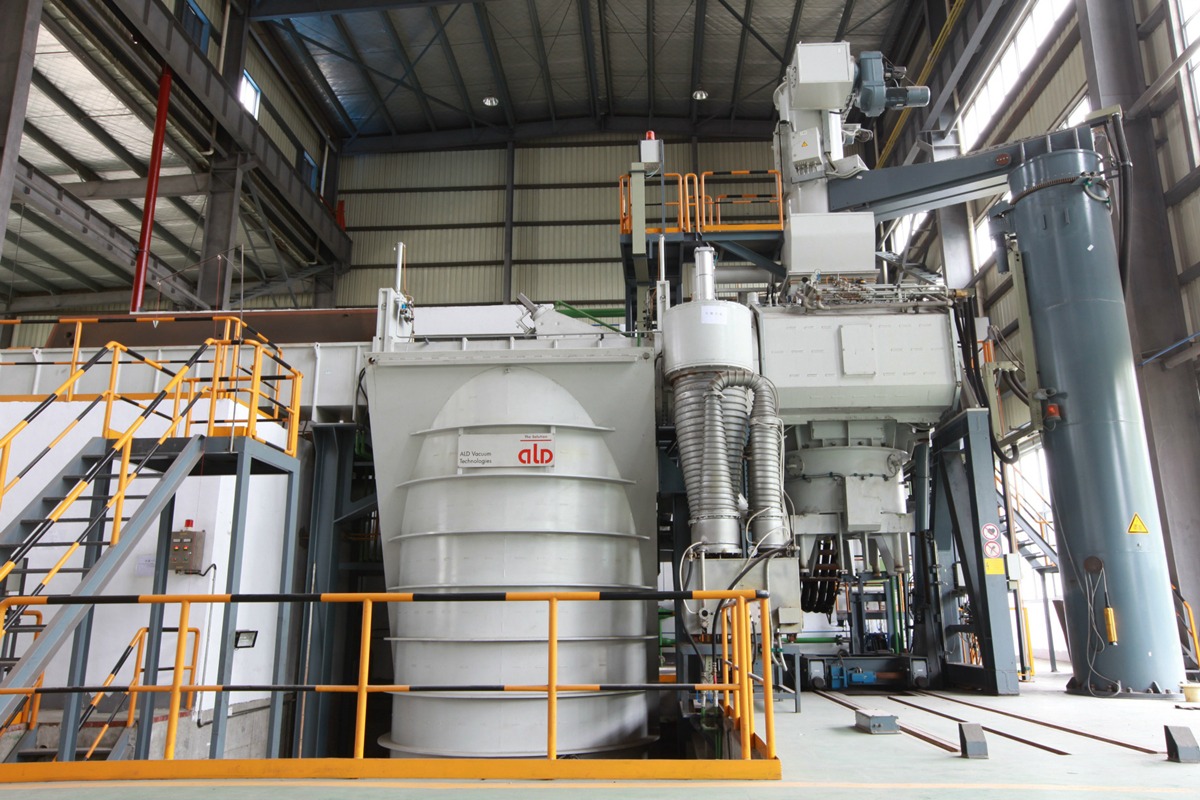

learn more
Manufacturing Equipments
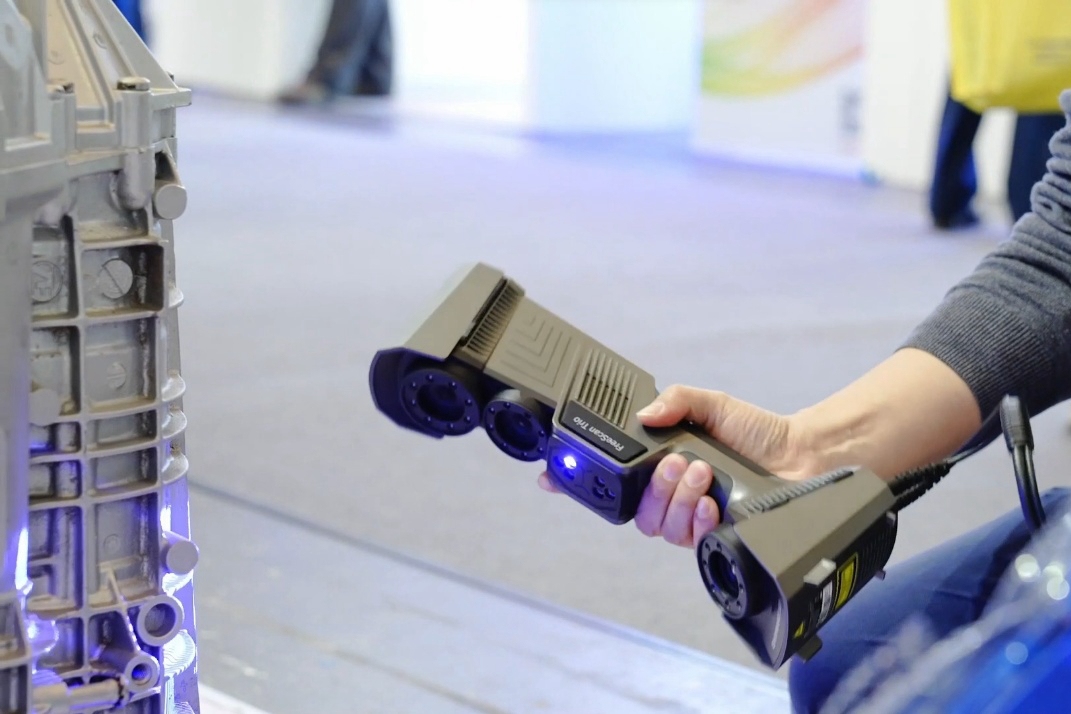

learn more
Testing Equipments
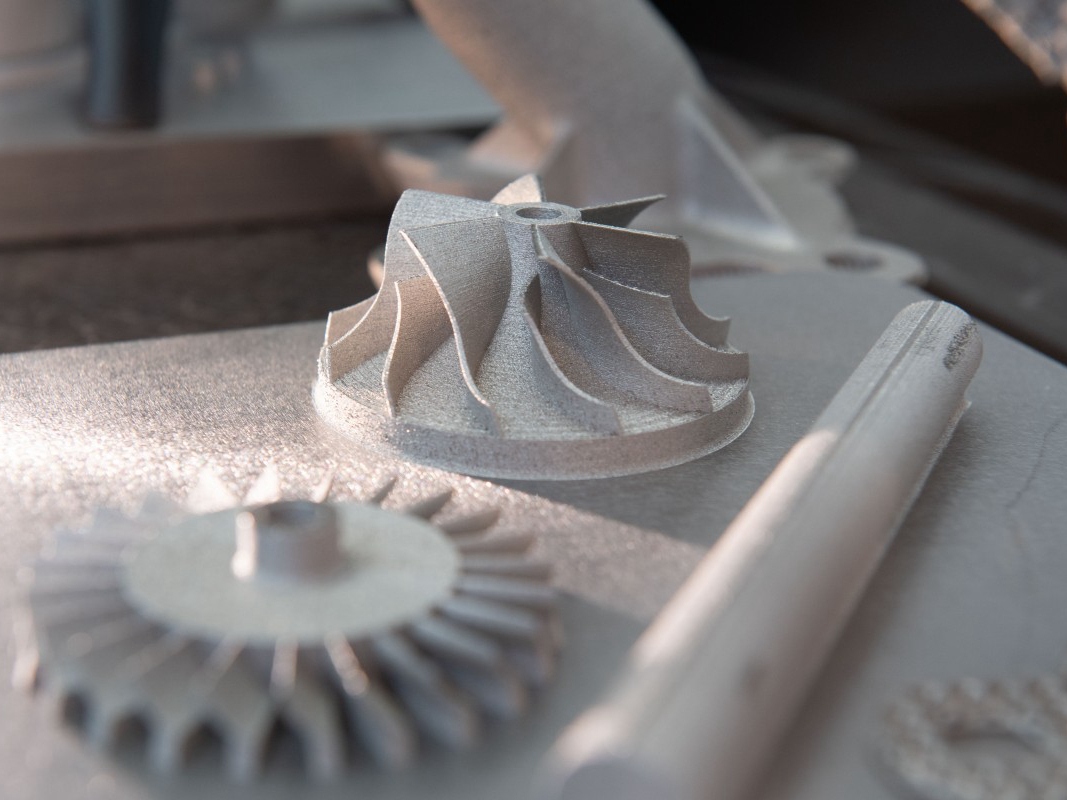

learn more
3D Printing Prototyping

learn more
FAQs

learn more
Contact
Let's Start A New Project Today