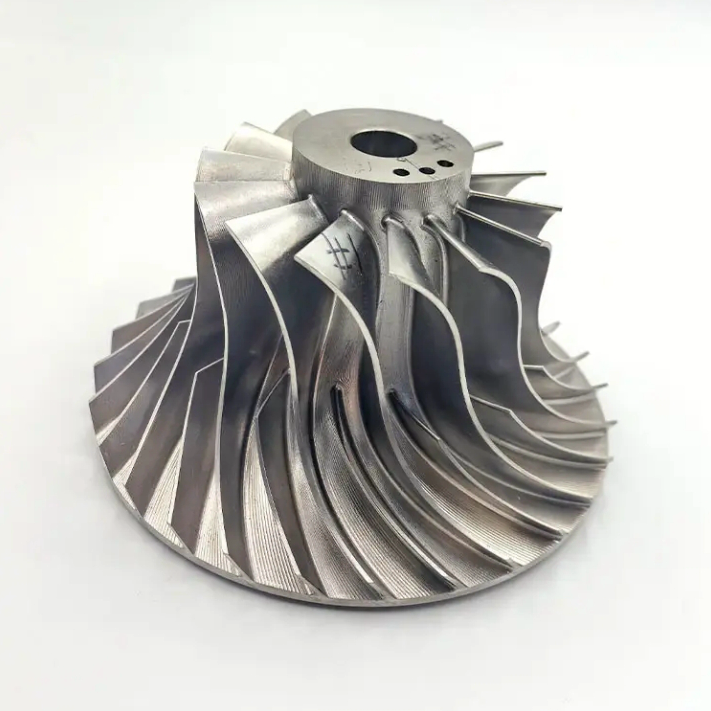
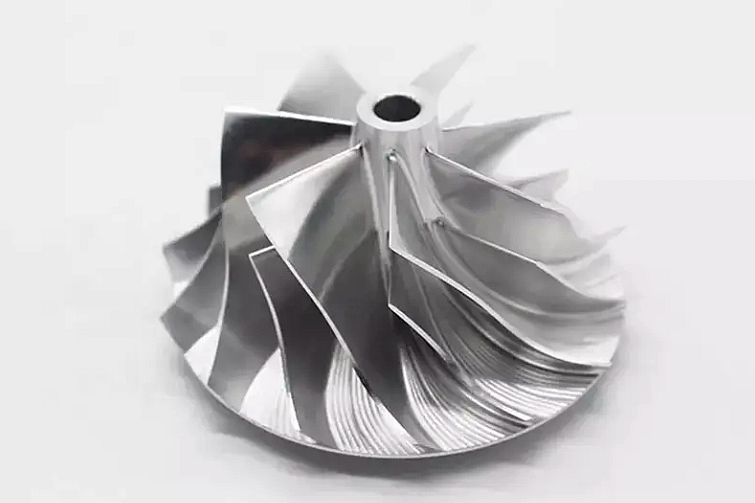
How Water Immersion Ultrasonic Inspection Benefits Superalloy CNC Machined Parts
Water immersion ultrasonic inspection (WUI) is a highly effective non-destructive testing (NDT) method widely used for inspecting superalloy components, particularly CNC machined parts. This technology provides a powerful means to detect subsurface defects, ensuring the integrity and reliability of high-performance materials used in aerospace and aviation, power generation, automotive, and defense industries.
In water immersion ultrasonic inspection, components are submerged in water while high-frequency sound waves are transmitted through the material. When the sound waves encounter an internal defect, such as a crack or void, they are reflected to the sensor, which analyzes the signals to identify and locate any flaws. This process is susceptible and can detect even the slightest internal anomalies in superalloy parts that may not be visible on the surface. The advantages of water immersion ultrasonic inspection over other methods include its ability to assess the integrity of complex geometries and hard-to-reach areas and its non-destructive nature, which allows the part to remain entirely usable after testing.
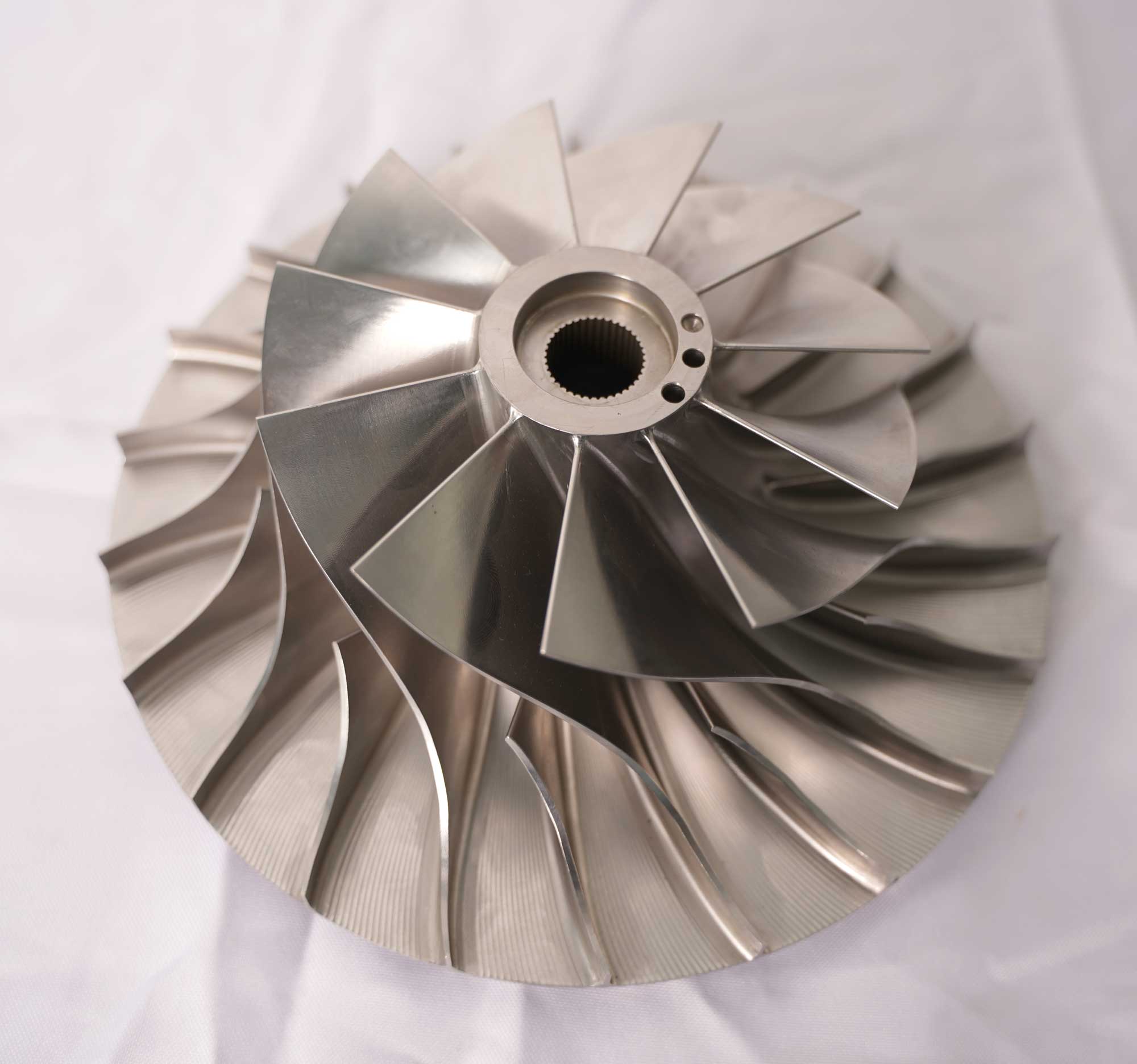

WUI is particularly beneficial for critical superalloy components used in applications such as turbine blades in aerospace, engine casings in power generation, and armor systems in military applications, where detecting subsurface defects is crucial for ensuring safety and performance. This method provides manufacturers and engineers with the confidence that their superalloy components meet the required quality standards and are fit for service in demanding environments.
What is Water Immersion Ultrasonic Inspection?
Water immersion ultrasonic inspection is an advanced technique to detect internal and surface defects in materials using high-frequency sound waves. Unlike conventional ultrasonic testing, which typically requires direct contact with the part, water immersion ultrasonic inspection involves submerging the part in water or a liquid couplant. This creates an environment that enhances the clarity of sound wave transmission and allows for a more accurate detection of defects.
In water immersion ultrasonic testing, a transducer emits high-frequency sound waves that travel through the material. These waves are reflected to the transducer when they encounter a defect, such as a crack, void, or inclusion. These reflections are then analyzed to identify the defect's type, size, and location. The liquid medium helps transmit sound waves more efficiently, providing more precise and detailed results than dry ultrasonic testing.
The process is commonly used for inspecting a variety of high-temperature alloys, including superalloy castings, forged components, and CNC machined parts. Water immersion ultrasonic inspection is particularly beneficial for materials with complex geometries and high-stress resistance, such as those used in critical aerospace and power generation components.
The Function of Water Immersion Ultrasonic Inspection
Water immersion ultrasonic inspection offers several key benefits that make it an essential tool for manufacturing and quality assurance of superalloy components. One of the primary functions of this process is to detect subsurface defects that are not visible to the naked eye. These defects could include cracks, voids, porosity, or inclusions that could compromise the performance and reliability of a component, particularly in critical applications such as superalloy turbine blades.
The water immersion method enhances the sensitivity and resolution of the ultrasonic waves, allowing for more accurate identification of internal flaws. This is especially crucial when inspecting superalloy CNC machined parts, where the precision of the part’s dimensions and the integrity of the material are vital to its functionality. Water immersion ultrasonic inspection helps ensure that these parts meet the required quality standards and can withstand the extreme conditions they will face in their applications, such as those in the aerospace and energy sectors.
Additionally, water immersion ultrasonic testing provides a faster and more reliable means of inspecting components than traditional inspection methods. It can inspect large or complex parts, making it ideal for the diverse range of superalloy components used in aerospace, power generation, and automotive industries. This efficiency allows for high-throughput production while maintaining high-stress applications' quality and safety standards.
Which Superalloy Parts Are Needed?
Water immersion ultrasonic (WUI) inspection is a powerful technique for evaluating the internal integrity of superalloy components, particularly those used in high-performance applications. This non-invasive method helps identify defects that could compromise a part's strength, durability, and performance. The following superalloy parts are well-suited for WUI:
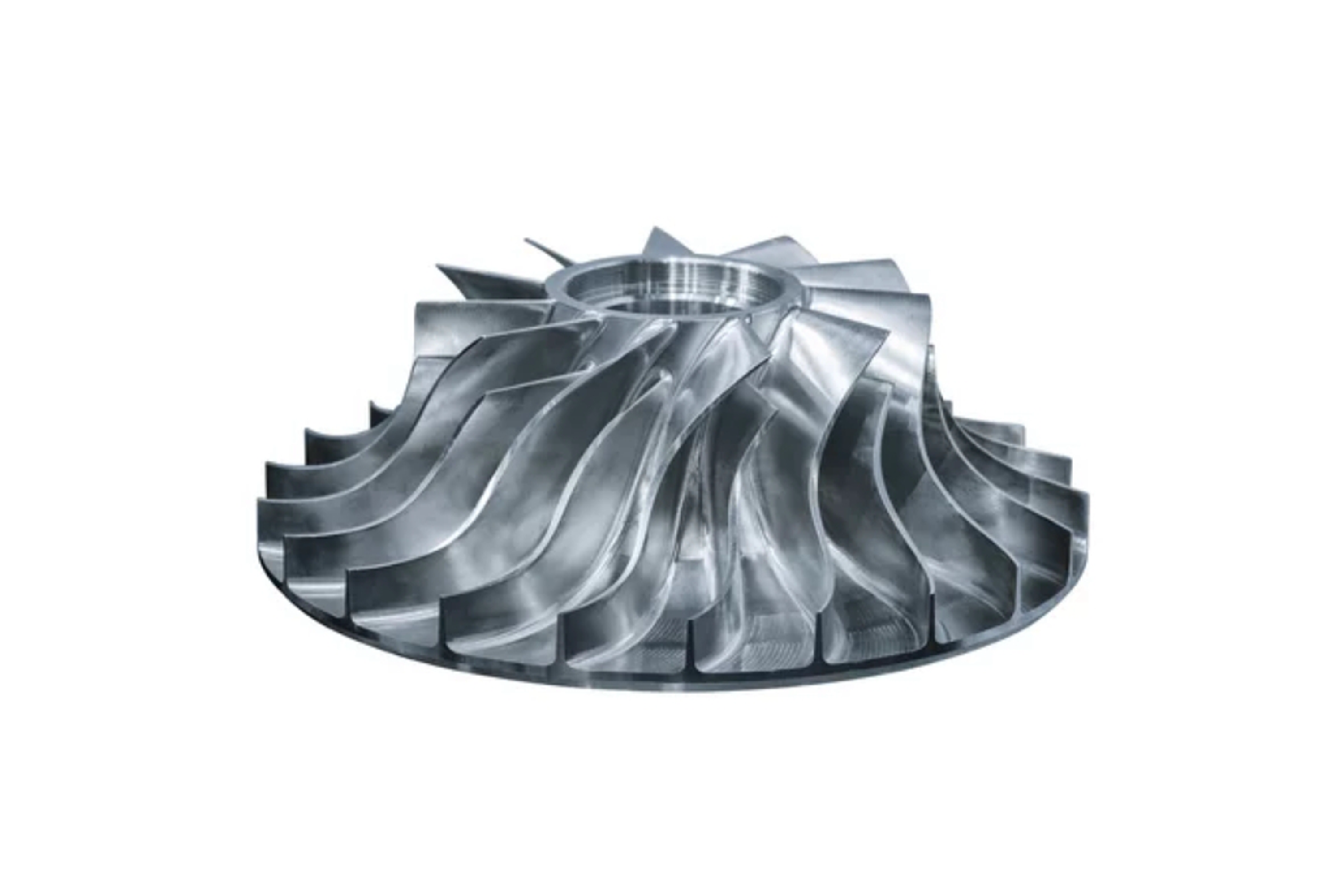
Superalloy CNC Machined Parts
Superalloy CNC machined parts, such as turbine blades, engine casings, and compressor blades, require precise geometries that are often difficult to inspect using traditional methods. These parts, made from high-performance materials like Inconel, CMSX, and Rene alloys, can be complex in shape and size. WUI provides a thorough examination, enabling the detection of internal defects such as cracks, porosity, and inclusions that might not be visible on the surface. By identifying these issues early, manufacturers can ensure that the CNC machined parts meet the stringent performance requirements for aerospace and other critical industries.
Superalloy Castings
Casting is a standard manufacturing method for large, intricate superalloy parts, including turbine blades, combustion chambers, and other aerospace components. Defects such as shrinkage cavities, porosity, and voids can occur during casting, mainly as the material cools. Superalloy castings are especially prone to internal flaws, which can compromise mechanical properties. WUI is an effective tool for inspecting these castings, ensuring that imperfections are detected before the part enters service. This helps guarantee that cast components meet the high-performance standards for critical applications like aerospace engines.
Superalloy Forging Parts
Forged superalloy parts, including turbine discs, shafts, and gears, are subjected to extreme mechanical forces during the forging process and their operational use. Superalloy forging can sometimes introduce subsurface defects, such as cracks or voids, which might not be visible externally but can cause catastrophic failure under load. Water immersion ultrasonic inspection is ideal for detecting these flaws, allowing manufacturers to assess the internal integrity of forged components before they are put into service. By identifying any weaknesses early, WUI helps prevent costly repairs and ensures the longevity and safety of critical parts used in high-stress environments.
3D Printed Superalloy Parts
With the growing use of 3D printed superalloy parts in aerospace and defense, especially for complex geometries and customized components, ensuring the internal quality of these parts is crucial. Additive manufacturing can lead to defects like porosity, cracks, and irregularities in material deposition. Traditional inspection methods often struggle with these complex internal structures. WUI offers an effective solution for inspecting 3D printed superalloy components, ensuring that these parts meet the required strength, integrity, and performance standards.
By leveraging water immersion ultrasonic inspection for superalloy castings, CNC machined parts, forged components, and 3D printed parts, manufacturers can ensure that their superalloy components are free from defects that could impact their performance and safety. This technology is critical in maintaining the integrity of parts used in demanding industries such as aerospace, energy, and defense.
Compared with Other Processes
When comparing water immersion ultrasonic inspection with other traditional inspection methods, several key advantages stand out.
Traditional Ultrasonic Testing vs. Water Immersion Ultrasonic Testing
Traditional ultrasonic testing (dry testing) involves placing a transducer directly on the material's surface and sending sound waves through it. While this method can be effective, it does not provide the same clarity or sensitivity as water immersion ultrasonic testing. Water immersion improves the transmission of sound waves by eliminating air gaps between the transducer and the part, leading to better defect detection, particularly in larger or more complex components. The liquid coupling also allows for more precise and consistent results, making it ideal for high-performance superalloy parts.
X-ray Inspection
X-ray inspection is another standard method for detecting internal defects in materials. While X-ray can provide high-resolution images, it requires specialized equipment and is typically slower than ultrasonic testing. Moreover, X-ray inspection is less effective for detecting certain flaws, such as porosity or inclusions; ultrasonic waves may better capture that. Water immersion ultrasonic inspection, on the other hand, is faster, more efficient, and can provide more detailed results for specific defect types, such as microcracks or voids that might affect superalloy components.
Eddy Current Testing
Eddy current testing is primarily used for surface defect detection and is effective for thin materials. However, it is less effective at detecting subsurface defects or deeper flaws within the material. Water immersion ultrasonic testing is superior for detecting internal defects in superalloy parts, particularly in thicker materials where eddy current testing may not provide sufficient resolution.
X-ray CT Scanning
X-ray computed tomography (CT) scanning provides 3D imaging of the internal structure of a part, but it is typically slower and more expensive than ultrasonic inspection methods. While CT scanning can provide detailed insights into a part’s internal geometry, water immersion ultrasonic inspection is generally more cost-effective and faster for detecting common flaws like cracks, voids, and inclusions in superalloy components.
Industry and Application
Water immersion ultrasonic inspection is critical in industries that rely on superalloy components for their high performance and durability. Here are some of the key sectors and applications where this technology is particularly beneficial:
Aerospace
In the aerospace industry, components like turbine blades, engine casings, and combustion chambers are subjected to extreme conditions, including high temperatures, pressures, and mechanical stresses. Any defect in these components can lead to catastrophic failure. Water immersion ultrasonic inspection (WUI) ensures these critical parts are accessible from internal flaws that could jeopardize their safety and performance. For example, superalloy turbine blades are inspected using WUI to detect minute internal cracks or voids, ensuring their reliability in commercial and military aviation.
Power Generation
In power generation, power plants' turbine discs, rotors, and heat exchangers must withstand high stresses and temperatures. WUI ensures the integrity of these components by detecting cracks, voids, and other defects that could reduce their lifespan or cause failures during operation. For instance, superalloy turbine discs and rotors are critical for power generation, and WUI helps detect internal flaws early, ensuring their continued efficiency and safety.
Automotive
In the automotive industry, superalloy parts such as pistons, turbochargers, and engine blocks are subjected to high pressures and temperatures. WUI helps detect defects like cracks or voids in these components that could compromise their performance, leading to engine failures or reduced efficiency. Early detection ensures that parts like high-temperature alloy turbochargers and pistons meet stringent quality standards, contributing to engine reliability and performance.
Oil & Gas
Superalloy components used in the oil and gas industry, such as pump parts, valves, and pressure vessels, operate in highly demanding environments. WUI ensures these components are free from defects that could lead to leakage or failure under pressure. For example, superalloy pump components undergo rigorous ultrasonic testing to identify flaws early, preventing costly repairs and downtime in critical oil and gas operations.
Marine
Water immersion ultrasonic testing (WUI) is also used in the marine industry to inspect propulsion systems, turbines, and engine parts. Given the harsh operating conditions in marine environments, ensuring the structural integrity of these components is vital for safety and performance. For instance, superalloy turbine blades in naval vessels undergo WUI to detect any internal cracks or weaknesses, ensuring their functionality and longevity in demanding marine environments.
Defense and Military
In defense and military applications, superalloy parts are used in systems requiring the highest reliability levels, including missile systems, armored vehicles, and military aircraft. WUI ensures that these critical components are free from defects that could affect their performance in the field. For example, superalloy missile segments are inspected using WUI to identify potential internal defects, ensuring the safety and effectiveness of military assets in high-risk situations.
Water immersion ultrasonic inspection is a non-destructive testing method that is essential in ensuring superalloy components' safety, durability, and performance across these industries. By identifying internal flaws and defects early, this technology helps prevent costly failures and ensures the reliability of critical components in high-stress applications.
FAQs
How does water immersion ultrasonic inspection detect internal defects in superalloy parts?
What types of superalloy parts benefit most from water immersion ultrasonic testing?
How does water immersion ultrasonic inspection compare to other non-destructive testing methods like X-ray or eddy current testing?
Can water immersion ultrasonic inspection be used on 3D printed superalloy components?
What industries rely most on water immersion ultrasonic inspection for their superalloy parts?